What is IUI ?
Intra Uterine insemination (IUI) with either husband or donor sperm is a procedure done in the clinic. IUI is basically artificial insemination procedure in which washed sperm directly into the uterine cavity. In IUI cycle we try to create the best possible chances of conception and implantation. By giving stimulation medicines we ensure good number of follicles are recruited for development and that best possible follicular growth occurs. Estrogen released by growing follicles plays a direct role in thickening of the endometrial lining which is essential for implantation. If good number of follicles are recruited, the endometrial will also achieve the desired thickness (> 7mm). The semen sample is washed to remove any bad sperms and the best sperms are separated and inserted into the uterus at the best possible time (on the day of ovulation).
When is IUI recommended ?
Sexual disorders like impotence, premature ejaculation, erectile disorder, vaginismus, neurological disorders etc.
Cervical factors like cervical stenosis, infections, highly acidic cervical mucus, or presence of anti-sperm antibodies — IUI helps by bypassing the cervix and placing washed motile sperms directly into the uterus.
Ovulatory disorders that can be corrected with ovarian stimulation.
Grade 1 endometriosis, provided the fallopian tubes are patent.
Age-related fertility decline — stimulation injections can improve success.
Male sub-fertility where sperm count and motility are low — IUI helps by placing washed motile sperm directly into the uterus close to the oocyte.
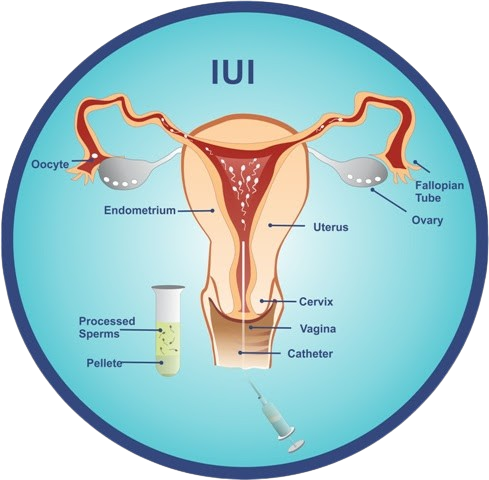
What to expect?
An IUI cycle can be broadly broken down into the following stages:
Ovarian Stimulation
Ovulation cycle Monitoring
Trigger
IUI
Typically an IUI cycle last 15 days that is from the Day 2 to Day 15.
D2-D6: Stimulation medicines are started from D2. Based on the protocol and cost that the patient can afford, the protocol may be based only on medicines or a combination of medicines + stimulation injections or based only on Stimulation drugs. Based on the protocol the medicines have to be continued form D2 till the date advised by the fertility specialist.
D9-D12: Follicular scans are started form D9 and done on alternate days or on intervals decided by the doctor till D12 OR D13.
D12: Once the follicles achieve the desired size, Trigger is induced by giving HCG injection. In 90% of cases Trigger happens on D12. Ovulation occurs within 36 hours of Trigger.
D13-14: Another scan is done to check if the ovulation has occurred. If yes IUI is done on the same day. Else the IUI is scheduled on day 14.
Note: Depending on the stimulation protocol (what kind of medicines are prescribed) frequency of scans and the duration of taking the medicines would vary.
Instructions for Husband before semen collection:
Do not have intercourse for 2–3 days before the day of collection.
The total number of days since last ejaculation should be no longer than 4–5 days. Sperm cells are made and replaced rapidly after each ejaculation. Prolonged abstinence (greater than 4 days) may increase the number of dead or poorly motile sperm cells.
It is extremely important to collect the semen specimen using sterile techniques. Bacteria that are normally found on the skin can contaminate the specimen if the container or semen come in contact with the skin. Samples with visible contamination of bacteria, yeast or other potentially infectious agents will not be processed!
Shower and wash well the morning of your appointment. Rinse all traces of soap from the body since soap contamination will kill sperm cells.
Instructions for Wife before IUI:
Some antibiotics are given in the initial part of treatment to take care of infections. It is important that both partners take the medications. Make sure you understand correctly what medications are required to be taken.
For your convenience, injections are available at the Centre at wholesale rates. There is however NO COMPULSION that you have to buy medicines from the centre.
Subcutaneous injections should be given under the skin, either on the forearm or the thigh. Spirit should not be used to clean the area.
It is important that you and your partner 'stay together' on either Day 7 or Day 8 of the periods so that the semen sample on the day of IUI is between 3 to 7 days old.
Once the eggs are mature (average of 18 - 20 mm size), an HCG injection would be given to you to release the mature eggs. If at any point of time after the injection you feel any pain in the lower part of your tummy, call the doctor immediately. The IUI may need to be re-scheduled.
IUI does not require any admission in the Nursing Home. However, do come with 2–3 hours in hand.
Inform the Centre once your periods start so that a booking for Follicular Study (Ultrasonography) can be made on Day 2 and then again on Day 10. If it happens to be a Sunday, come on Saturday, not Monday.
After IUI, a medication needs to be inserted vaginally twice a day. In the morning, lie down for one hour after the insertion. At night, insert at the time of going to bed. Some of the medication may come out in a liquid form, do not get alarmed.
What is the process of IUI with donor sperm?
The Treatment protocol of the wife remains the same. On the day of IUI the donor sperm needs to be thawed. It then undergoes sperm washing and the prepared donor sample is transferred into the uterus.
Where is the sperm collected? How long before the IUI?
Usually the sample is collected through ejaculation by masturbation into a sterile semen collection container in a private room at the clinic. From the time the sample is received, it takes about 1 hour 30 minutes to make the sample ready for insemination. The amount of time may vary depending on the sperm quality, as special techniques may be required.
How long before an IUI should the male abstain from intercourse/ejaculating and store up sperm?
This depends on your individual situation, but it usually should not be less than 3 days and not more than 7 days in order to ensure the best motility and morphology. We advise that you have an intercourse around the 7th or 8th day of your cycle and then abstain.
How long after IUI should implantation occur?
Implantation takes place 6-12 days after ovulation - so 6-12 days after a well-timed IUI.
What kind of monitoring is usually done for an IUI cycle?
Transvaginal Ultrasonography is done from Day 10 or 11 of the menstrual cycle to note the growth in follicular size and look for signs of ovulation like reduction in size of follicle, fluid in POD etc.
At what size are follicles considered mature?
Follicles are usually considered mature once they have achieved a size of about 18 mm. Also, follicles continue to grow until they release, usually at a rate of about 1-2 mm per day. A woman may ovulate more than one follicle in a cycle, but the releases will occur within 24 hours. When HCG is not used, only follicles close in size are likely to release. The use of HCG induces ovulation in about 95 percent of women, and will get most mature follicles to rupture.